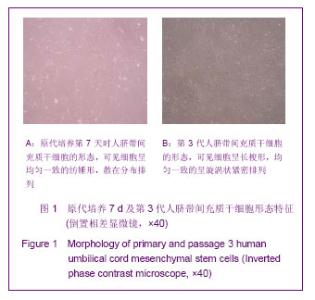
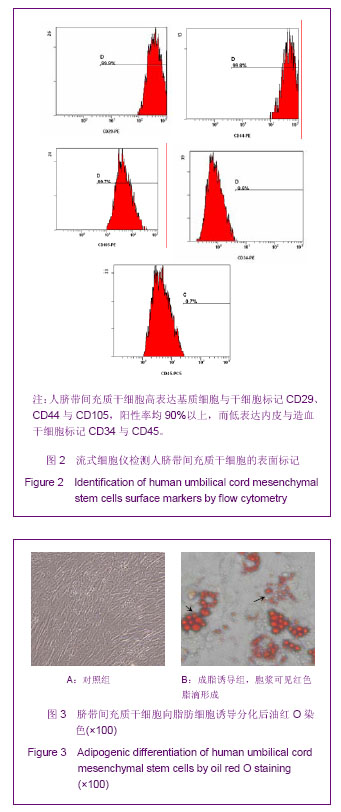
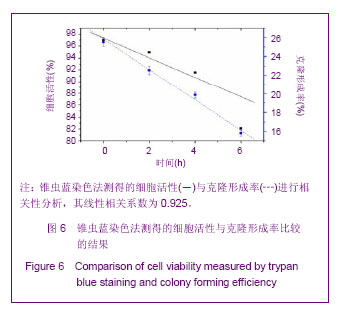
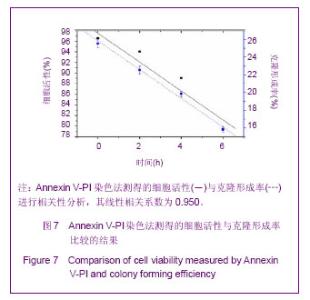
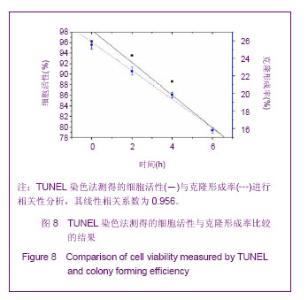
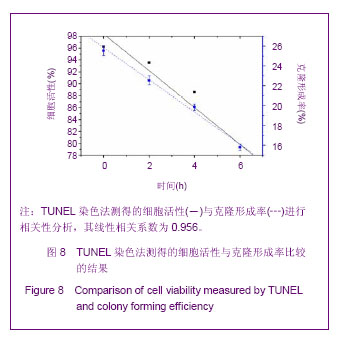
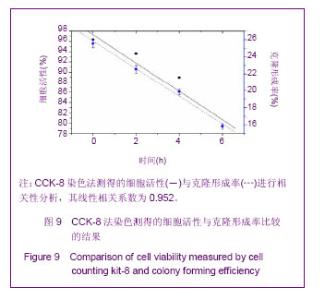
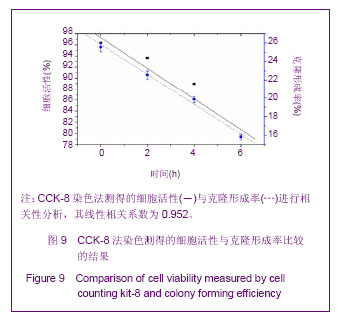
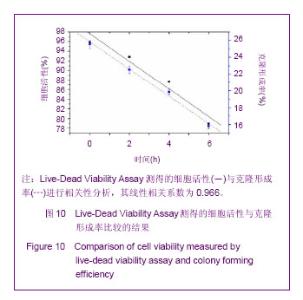
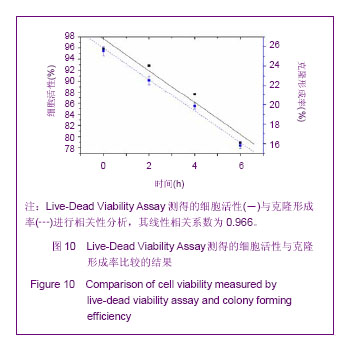
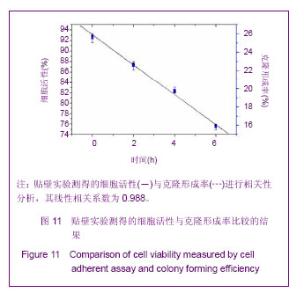
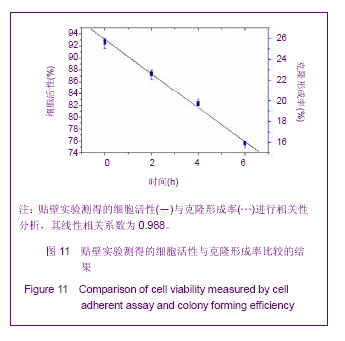
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (32): 5847-5854.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.32.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Evaluation indexes for the viability of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells before transplantation
Lei Xin1, Chen Yan2, Zhang Jian-lin1, Cui Lei2, Niu Yu-hu1, Niu Bo1
- 1Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
2Department of Respiratory Medicine, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2012-12-03Revised:2012-12-10Online:2013-08-06Published:2013-08-06 -
Contact:Niu Bo, M.D., Doctoral supervisor, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China niub2004@126.com -
About author:Lei Xin★, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China leejunkilx@sina.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lei Xin, Chen Yan, Zhang Jian-lin, Cui Lei, Niu Yu-hu, Niu Bo. Evaluation indexes for the viability of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells before transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(32): 5847-5854.
share this article
| [1] Lee JW, Fang X, Krasnodembskaya A, et al. Concise review: Mesenchymal stem cells for acute lung injury: role of paracrine soluble factors. Stem Cells. 2011;29(6):913-919.[2] Semenov OV, Koestenbauer S, Riegel M, et al. Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from human placenta: critical parameters for isolation and maintenance of stemness after isolation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;202(2):193.e1- 193.e13.[3] Tran CT, Huynh DT, Gargiulo C,et al. In vitro culture of Keratinocytes from human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells: the Saigonese culture. Cell Tissue Bank. 2011; 12(2):125-133.[4] Can A, Balci D. Isolation, culture, and characterization of human umbilical cord stroma-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;698:51-62.[5] Singleton PA, Salgia R, Moreno-Vinasco L,et al. CD44 regulates hepatocyte growth factor-mediated vascular integrity. Role of c-Met, Tiam1/Rac1, dynamin 2, and cortactin. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(42):30643-30657.[6] Mei SH, McCarter SD, Deng Y, et al. Prevention of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing angiopoietin 1. PLoS Med. 2007;4(9):e269.[7] Manning E, Pham S, Li S, et al. Interleukin-10 delivery via mesenchymal stem cells: a novel gene therapy approach to prevent lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. Hum Gene Ther. 2010;21(6):713-727.[8] Olson AL, Swigris JJ. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and epidemiology. Clin Chest Med. 2012;33(1):41-50.[9] Cho PS, Messina DJ, Hirsh EL,et al. Immunogenicity of umbilical cord tissue derived cells. Blood. 2008;111(1):430- 438.[10] La Rocca G, Anzalone R, Corrao S, et al. Isolation and characterization of Oct-4+/HLA-G+ mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord matrix: differentiation potential and detection of new markers. Histochem Cell Biol. 2009;131(2): 267-282.[11] Venkataramana NK, Kumar SK, Balaraju S,et al. Open-labeled study of unilateral autologous bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in Parkinson's disease.Transl Res. 2010;155(2):62-70.[12] Garzón I, Pérez-Köhler B, Garrido-Gómez J, et al. Evaluation of the cell viability of human Wharton's jelly stem cells for use in cell therapy.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2012;18(6): 408-419.[13] Rodriguez-Morata A, Garzon I, Alaminos M, et al. Cell viability and prostacyclin release in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Ann Vasc Surg. 2008;22(3):440-448.[14] Mazaheri Z, Movahedin M, Rahbarizadeh F, et al. Different doses of bone morphogenetic protein 4 promote the expression of early germ cell-specific gene in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2011; 47(8):521-525. [15] Sadan O, Shemesh N, Barzilay R,et al. Migration of neurotrophic factors-secreting mesenchymal stem cells toward a quinolinic acid lesion as viewed by magnetic resonance imaging.Stem Cells. 2008;26(10):2542-2551.[16] Seeger FH, Tonn T, Krzossok N, et al. Cell isolation procedures matter: a comparison of different isolation protocols of bone marrow mononuclear cells used for cell therapy in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2007;28(6):766-772.[17] Mihu CM, Mihu D, Costin N, et al. Isolation and characterization of stem cells from the placenta and the umbilical cord. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2008;49(4):441-446.[18] Horwitz EM, Le Blanc K, Dominici M, et al. Clarification of the nomenclature for MSC: The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2005;7(5):393-395.[19] Heng BC, Cowan CM, Basu S.Temperature and calcium ions affect aggregation of mesenchymal stem cells in phosphate buffered saline.Cytotechnology. 2008;58(2):69-75.[20] 卢润章,赵经慧,程梅,等.人脐带间充质干细胞体外培养的生物学特性研究[J].黑龙江医学,2013,37(2):81-83.[21] 张芬熙,洪艳,梁文妹.人脐带间充质干细胞的分离培养及超微结构特点研究[J].贵阳医学院学报,2013,38(1):5-9,15.[22] 赵庆华,祝加学,王雷,等.人脐带间充质干细胞的生物学特性及向软骨细胞、骨细胞分化实验研究[J].中华医学杂志,2011,91(5): 317-321.[23] 孙丽,于丽,张华芳,等.人脐带间充质干细胞的分离培养及生物学特性[J].解剖科学进展,2011,17(2):131-134.[24] Mazaheri Z, Movahedin M, Rahbarizadeh F,et al. Different doses of bone morphogenetic protein 4 promote the expression of early germ cell-specific gene in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2011; 47(8):521-525.[25] Guo RM, Cao N, Zhang F,et al.Controllable labelling of stem cells with a novel superparamagnetic iron oxide-loaded cationic nanovesicle for MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 2012;22(11): 2328-2337.[26] Sun JH, Zhang YL, Qian SP,et al.Assessment of biological characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells labeled with superparamagnetic iron oxide particles in vitro.Mol Med Rep. 2012;5(2):317-320.[27] Mascotti K, McCullough J, Burger SR. HPC viability measurement: trypan blue versus acridine orange and propidium iodide.Transfusion. 2000;40(6):693-696.[28] 刘阳,赖翼,李敏惠,等.流式细胞术检测细胞存活率的方法学建立[J].国际检验医学杂志,2011,32(15):1663-1664.[29] Chan LL, Wilkinson AR, Paradis BD, et al. Rapid image-based cytometry for comparison of fluorescent viability staining methods. J Fluoresc. 2012;22(5):1301-1311.[30] van der Bogt KE, Schrepfer S, Yu J, et al. Comparison of transplantation of adipose tissue- and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the infarcted heart. Transplantation. 2009;87(5):642-652.[31] Assmus B, Tonn T, Seeger FH, et al. Red blood cell contamination of the final cell product impairs the efficacy of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55(13):1385-1394.[32] Song H, Cha MJ, Song BW, et al. Reactive oxygen species inhibit adhesion of mesenchymal stem cells implanted into ischemic myocardium via interference of focal adhesion complex. Stem Cells. 2010;28(3):555-563.[33] Sarugaser R, Lickorish D, Baksh D,et al. Human umbilical cord perivascular (HUCPV) cells: a source of mesenchymal progenitors.Stem Cells. 2005;23(2):220-229. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Liu Zhichao, Zhang Fan, Sun Qi, Kang Xiaole, Yuan Qiaomei, Liu Genzhe, Chen Jiang. Morphology and activity of human nucleus pulposus cells under different hydrostatic pressures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1172-1176. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [5] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [6] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [7] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [8] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [9] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [10] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [11] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [12] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [13] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [14] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [15] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||